PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
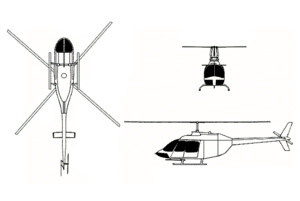
OH-58 Kiowa
| OH-58 Kiowa | |
|---|---|
| OH-58D Kiowa Warrior | |
| Type | Observation/scout helicopter |
| Manufacturer | Bell Helicopter Textron |
| Maiden flight | 1962 |
| Introduced | 1967 |
| Status | Active service |
| Primary users | United States Army Taiwan (Republic of China), Saudi Arabia |
| Produced | 1966-1989 |
| Number built | 2200+ |
| Developed from | Bell 206 |
The OH-58 Kiowa is a family of single-engine, single-rotor, observation and light attack helicopters manufactured by Bell Helicopter Textron and originally based on the company's Bell 206A JetRanger helicopter. The OH-58 is operated primarily by the United States Army and it's primary missions are reconnaissance, surveillance, and intelligence gathering.
Contents
Development
Light Observation Helicopter (LOH)
In October 1961, the Army submitted a request for proposals (RFP) for the Light Observation Helicopter (LOH). Bell, along with 12 other manufacturers (including Fairchild-Hiller and Hughes Tool Co. Aircraft Division), entered the competition.[1] Bell submitted their design for model 206, which was selected out of the design phase of the Navy-run competition by the Army[2] and designated as the YHO-4A.[3][4]
Bell produced 5 prototype aircraft in 1962 to submit to the Army for the Test and Evaluation phase. That same year, all aircraft began to be designated according to the new Joint Services designation system, so the prototype aircraft were redesignated as YOH-4A. During the flight testing phase, the power problems of the YOH-4A eliminated it from consideration for selection.[5]
After the failed military contract bid, Bell attempted to market the model 206, but it didn't fare well at all commercially. Bell's market research showed that it was the body design that customers found mostly unpalatable. When Bell redesigned the body of the airframe to a more sleek and aesthetic design and reintroduced it as model 206A, the JetRanger was born and Bell found they had a commercial success on their hands.[6]
In 1967, the Army reopened the LOH competition for bids because Hughes Tool Co. Aircraft Division couldn't meet the contractual production demands.[citation needed] Bell resubmitted for the program using their model 206A design.[3] Fairchild-Hiller failed to resubmit their bid with the YOH-5A, which they had successfully marketed as the FH-1100.[7] In the end, Bell underbid Hughes to win the contract and the model 206A was designated as the OH-58A. Following the U.S.Army's naming convention for helicopters, the OH-58A was named Kiowa in honor of the Native American tribe.[citation needed]
Army Helicopter Improvement Program (AHIP)
In the 1970s, the U.S. Army began evaluating the need to improve the capabilities of their scout aircraft. The OH-58A and OH-58C lacked the power for operations in areas that exposed the aircraft to high altitude and hot temperatures. The power shortcoming caused other issues as the AH-64A replaced the venerable AH-1 in the Attack battalions of the Army. To solve the problem, the Army had been searching for a solution called the Advanced Scout Helicopter (ASH), but when the program proved too expensive, the Army opted for a more affordable solution, the Army Helicopter Improvement Program (AHIP). Once again, Bell's design faced off with the Hughes' design. Bell Helicopter Textron offered a more robust version of the OH-58 in their model 406 aircraft, and Hughes Helicopters offered an upgraded version of the OH-6, and in September 1981, Bell Helicopter Textron was awarded a development contract.[8] The prototype flew in 1983, and the aircraft entered service in 1985 as the OH-58D.[9]
Initially intended to be used in attack, cavalry and artillery roles, the Army only approved a low initial production level and confined the role of the OH-58D to field artillery observation. The Army also directed that a follow-on test be conducted to further evaluate the aircraft due to perceived deficiencies. On 1 April 1986, the Army formed a task force at Fort Rucker, Alabama, to remedy deficiencies in the AHIP.[9] Apparently, as a result of those deliberations, the Army had planned to discontinue the OH-58D in 1988 and focus on the LHX, but Congress approved $138 million for expanding the program, calling for the AHIP to operate with the Apache as a hunter/killer team; the AHIP would locate the targets, and the Apache would destroy them in a throwback to the traditional OH-58/AH-1 relationship.[10] However, based on experience with Task Force 118's performance operating armed OH-58D helicopters in the Persian Gulf in support of Operation Prime Chance, the Secretary of the Army directed that the aircraft's armament systems be upgraded and that the aircraft be used primarily for scouting and armed reconnaissance.[11]
RAID
In 1989, Congress mandated that the Army National Guard would be a player in the country's War on Drugs enabling them to aid federal, state and local law enforcement agencies with "special congressional entitlements". In response, the Army National Guard Bureau created the Reconnaissance and Aerial Interdiction Detachments (RAID) in 1992, consisting of aviation units in 31 states with 76 specially modified OH-58A helicopters to assume the reconnaissance/interdiction role in the fight against illegal drugs. During 1994 twenty-four states conducted more than 1,200 aerial counterdrug reconnaissance and interdiction missions, conducting many of these missions at night. Eventually, the program was expanded to cover 32 states and consists of 116 aircraft including dedicated training aircraft at the Western Army Aviation Training Site (WAATS) in Marana, Arizona.[12]
The RAID program’s mission has now been expanded to include the war against terrorism and supporting U.S. Border Patrol activities in support of homeland defense. The National Guard RAID units' Area of Operation (AO) is the only one in the Department of Defense that is wholly contained within the borders of the United States.[12]
Variants
OH-58A
The OH-58A Kiowa is a 4-place observation helicopter. The Kiowa has two-place pilot seating, although the controls in the left seat are designed to be removed to carry a passenger up front. Its primary mission is to locate the enemy and report the location and/or conduct calls for fire from artillery units nearby to destroy, disrupt or disable the enemy. During its Vietnam development, it was fitted with an M134 Minigun 7.62 mm electrically operated machine gun. In 1978, OH-58A aircraft began to be converted to the same engine and dynamic components as the OH-58C.[13]
74 OH-58A helicopters were delivered to the Canadian Armed Forces as COH-58A and redesignated as CH-136 Kiowa helicopters.[14] The Australian Army produced the OH-58A under contract in Australia as the CA-32. It was essentially the 206B-1 equivalent OH-58A (upgraded engine and longer rotor blades). The first twelve were built in the U.S. then torn down and shipped to Australia where they were reassembled.[15]
In 1992, 76 OH-58A were modified with an engine upgrade, a thermal imaging system, a communications package for law enforcement, enhanced navigational equipment and high skid gear as part of the Army National Guard's (ARNG) Counter-Drug RAID program. The program called for these "OH-58A+" aircraft to be located in 31 states and the Western Army Aviation Training Site (WAATS). By the end of the summer of 1994, 24 states had their detachments operational.[16] The program has currently been expanded to 32 states and a total of 116 aircraft.[12]
OH-58B
The OH-58B Kiowa was an export version for the Austrian Air Force.[17]
OH-58C

Equipped with a more robust engine, the OH-58C was supposed to solve many issues and concerns regarding the Kiowa's power. In addition to the upgraded engine, the OH-58C had unique IR suppression systems mounted on its turbine exhaust. Early "C" models featured flat-panel windscreens as an attempt to reduce glint from the sun, which could give away the aircraft's location to an enemy. The windscreens had a negative effect of limiting the forward view of the crew, a previous strength of the original design.
The aircraft were also equipped with an oversized instrument panel. The panel, roughly a third bigger than the OH-58A panel held oversized instruments; primarily for teaching students instrument flying fundamentals.[verification needed] The panel is also equipped with Night Vision Goggle (NVG) compatible cockpit lighting. The lights inside the aircraft are modified to prevent them from interfering with the aircrews' use of NVGs.[18] OH-58C aircraft were also the first U.S. Army scout helicopter to be equipped with the AN/APR-39 radar detector, a system which allowed the crew to know when there were anti-aircraft radar systems in proximity to the aircraft.[19]
Some OH-58C aircraft were armed with two AIM-92 Stingers. These aircraft are sometimes referred to as OH-58C/S, the "S" referring to the Stinger installation.[20] Called Air-To-Air Stinger (ATAS), the weapon system was intended to provide an air defense capability for the Kiowas as they pulled security on the flanks, while the Apaches destroyed tanks in the Engagement Area (EA).[verification needed]
OH-58D
The OH-58D (Bell Model 406) was the result of the Army Helicopter Improvement Program (AHIP). It was a serious re-thinking of what was needed to be an effective scout aircraft. An upgraded transmission and engine gave it the power it needed, and a four-bladed main rotor made it much quieter than the two-bladed OH-58C. In addition, the OH-58D included the most distinctive feature of the family – a Mast-Mounted Sight (MMS) above the rotor system with a gyro-stabilized platform containing a TeleVision System (TVS), a Thermal Imaging System (TIS), and a Laser Range Finder/Designator (LRF/D). These new features gave the aircraft the additional mission capability of target acquisition and laser designation in both day or night, and in limited-visibility and adverse weather.
15 copies of a modified version of the OH-58D (sometimes referred to as the MH-58D[5][21]) was sold to Saudi Arabia[22] as the Bell 406CS "Combat Scout". The MMS was removed and replaced with a Saab HeliTOW sight system[1] mounted on the roof of the aircraft, just above the left pilot seat.[2] It also had detachable weapon hardpoints on each side.
Kiowa Warrior
The Kiowa Warrior is the armed version of the OH-58D Kiowa. The main difference that distinguishes the Kiowa Warrior from the original AHIP aircraft is a universal weapons pylon found mounted on both sides of the aircraft. These pylons are capable of carrying combinations of Hellfire missiles, Air-to-Air Stinger (ATAS) missiles, 7-shot 2.75" (70mm) Hydra-70[23] rocket pods, and an M296 .50 caliber machine gun. The Kiowa Warrior upgrade also includes improvements in available power, navigation, communication and survivability, as well as modifications to improve the aircraft's deployability.[24]
Operators
- Australia[15]
- 161 Recce Squadron
- 162 Recce Squadron
- Austria
- Fliegerregiment 1 [3]
- Canada (1971-1995)
- 3 Canadian Forces Flying Training School [4]
- 400 Tactical Helicopter Squadron [5]
- 401 Tactical and Training Helicopter Squadron (disbanded 23 June 1996) [6]
- 403 (Helicopter) Operational Training Squadron [7]
- 408 Tactical Helicopter Squadron [8]
- 411 Tactical Helicopter Squadron (disbanded 23 June 1996) [9]
- 422 Tactical Helicopter Squadron (disbanded 16 August 1980) [10]
- 430 Tactical Helicopter Squadron (430e Escadron Tactique d'Hélicoptères) [11]
- 438 Tactical Helicopter Squadron [12]
- Dominican Republic[25]
- Saudi Arabia[22]
- 1st Aviation Battalion
- Taiwan (Republic of China)[26]
- 601st Air Cavalry Brigade
- 602nd Air Cavalry Brigade
- United States (current)
- OH-58A/C
- Eagle Flight Detachment, Fort Irwin
- Eagle Flight Detachment, Fort Polk
- Reconnaissance and Aerial Interdiction Detachments (RAID), 32 states
- OH-58D
- 1st Squadron, 6th Cavalry Regiment
- 2nd Squadron, 6th Cavalry Regiment
- 4th Squadron, 6th Cavalry Regiment
- 6th Squadron, 6th Cavalry Regiment
- 1st Squadron, 17th Cavalry Regiment
- 2nd Squadron, 17th Cavalry Regiment
- 3rd Squadron, 17th Cavalry Regiment
- 6th Squadron, 17th Cavalry Regiment
- 7th Squadron, 17th Cavalry Regiment
- OH-58A/C
Specifications
OH-58A Kiowa
General characteristics
- Crew: 1 pilot, 2 pilots, or 1 pilot and 1 observer
- Length: 32 ft 2 in (9.81 m)
- Rotor diameter: 35 ft 4 in (10.77 m)
- Height: 9 ft 7 in (2.92 m)
- Empty weight: 1,553 lb (704 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 2313 lb (1049 kg)
- Powerplant: 1× Allison T63-A-700 turboshaft, 317 shp (236 kW)
- Fuel capacity: 70 gal (264.9 liters)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 120 knots (222.2 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 102 knots (188.9 km/h)
Armament
- M134 7.62 mm "Mini-gun"
or
- M129 40 mm Grenade Launcher
OH-58D Kiowa Warrior
General characteristics
- Crew: 2 pilots
- Length: 40 ft 8 in (12.39 m)
- Rotor diameter: 35 ft 0 in (10.67 m)
- Height: 7 ft 6 in (2.29 m)
- Empty weight: 3,290 lb (1,490 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 5,500 lb (2,495 kg)
- Powerplant: 1× Rolls-Royce T703-AD-700A or 250-C30R/3 turboshaft, 650 eshp (485 kW)
- Fuel capacity: 110 US gal (454 L)
Performance
- Maximum speed: 138 mph (222 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 120 mph (195 km/h)
- Range: 345 mi (556 km)
- Service ceiling: 20,500 ft (6,250 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,615 ft/min (8.2 m/s)
Armament
The OH-58D Kiowa Warrior can carry two weapons systems at one time (one on each pylon), among four different weapon systems:
- AGM-114 Hellfire anti-tank missiles in 2-count launchers
- Hydra 70 2.75 in (70 mm) rockets in 7-shot pods
- XM296 .50cal (12.7 mm) machine gun, 500 rounds (ammo can capacity) mounted only on the left side
- AIM-92 Stinger air-to-air missiles in 2-count launchers
References
- ↑ Steve Remington. The Cessna CH-1 Helicopter. CollectAir (commercemarketplace.com).
- ↑ George A. Spangenberg. "George A. Spangenberg Oral History".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Robert Beechy (18 November 2005). U.S Army Aircraft Acquisition Programs. Uncommon Aircraft 2006. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "LOH-1" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Rotary Aircraft Designation Crosswalk. GlobalSecurity.org.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Johan Visschedijk (16 October 2003). Bell 206 JetRanger.
- ↑ American Helicopter Museum: Bell 206 JetRanger.
- ↑ Michael J. Hirschberg and David K. Daley (7 July 2000). US and Russian Helicopter Development In the 20th Century.
- ↑ COL Robert S. Fairweather Jr. and MAJ Grant Fossum (July /August 1982). "The AHIP: Field Artillery Aerial Observer Platform of the Future" (pdf). Field Artillery Magazine.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Department of the Army Historical Summary, 1986.
- ↑ Department of the Army Historical Summary, 1988. U.S. Army Center of Military History.
- ↑ Department of the Army Historical Summary, 1989. U.S. Army Center of Military History.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Doug Nelms (1 November 2002). Homeland Defense:Fighting Homeland Wars. Rotor & Wing (www.aviationtoday.com).
- ↑ Department of the Army Historical Summary, 1978. U.S. Army Center of Military History.
- ↑ Bell CH-136 Kiowa. Air Force Public Affairs, Department of National Defence (15 APR 2004).
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 History of Bell OH58-A Kiowa Helicopter. 161 Possums. 161 Recce Association.
- ↑ Department of the Army Historical Summary, 1994.
- ↑ OH-58B Kiowa. GlobalSecurity.org.
- ↑ Template:Web cite
- ↑ Template:Web cite
- ↑ Team Redstone's Role in Operation DESERT SHIELD/DESERT STORM. Redstone Arsenal.
- ↑ MH-58D Combat Scout.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Royal Saudi Air Arms. Scramble. Dutch Air Society.
- ↑ Hydra-70 Rocket System. Federation of American Scientists.
- ↑ OH-58D Kiowa Warrior. Federation of American Scientists. Retrieved on 4 October 2006.
- ↑ Inigo Guevara (01 Sep 2003). Dominican Republic since 1945. Air Combat Information Group (acig.org).
- ↑ Republic of China Army Aviation. TaiwanAirPower.org.
External links
Related content
Related development
Comparable aircraft
Designation sequence
Related lists
See also
Fighter aircraft: YFM-1 · P-39 · P-59 · P-63 · XP-77 · XP-83
Commercial Helicopters: 47 · 204 · 205 · 206 · 210 · 212 · 214 · 222 · 230 · 407 · 412 · 417 · 427 · 429 · 430
Military Helicopters: H-13 · UH-1 · 207 · 209 · AH-1 · 309 · YAH-63 · OH-58 · ARH-70
Tiltrotors: V-22 · BA609 · TR918 · QTR
Experimental aircraft: X-1 · X-2 · X-5 · X-20 X-22 · XV-3 · XV-15 · 533 ·
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |
- Pages with reference errors
- Pages with broken file links
- Articles with unsourced statements since February 2007
- All articles with unsourced statements
- Wikipedia articles needing factual verification
- Military helicopters
- U.S. military reconnaissance aircraft 1960-1969
- U.S. military reconnaissance aircraft 1980-1989
- Active United States military aircraft