PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
XP-79 Flying Ram
| XP-79 Flying Ram | |
|---|---|
| Type | Interceptor |
| Manufacturer | Northrop |
| Designed by | Jack Northrop |
| Maiden flight | 12 September 1945 |
| Retired | 12 September 1945 |
| Status | Prototype |
| Primary user | U.S. Army Air Force |
| Number built | 1 |
| Developed from | Northrop MX-324 |
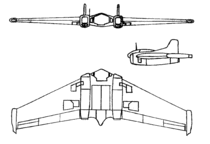
The Northrop XP-79 Flying Ram was an ambitious American design for a flying wing fighter aircraft; it had several notable design features. Among these, the pilot would operate the aircraft from a prone position – permitting the pilot to withstand much greater g-forces.
Contents
Design and development
In 1942, John K. Northrop conceived the XP-79 as a high-speed rocket powered flying wing fighter aircraft.
In January 1943, a contract for three prototypes designation XP-79 was issued by the USAAF.
To test the radical design, glider prototypes were built. One designated MX-324 was towed into the air on 5 July, 1944 by a P-38 making it the first rocket-powered aircraft built by America to fly.[1]
Originally it was planned to use a 2,000 lbf (9 kN) thrust XCALR-2000A-1 rocket motor supplied by Aerojet that used monoethyl aniline and a red fuming nitric acid, because of the corrosive and toxic nature of the liquids, the XP-79 was built using a welded magnesium alloy monocoque structure (to protect the pilot if the plane was damaged in combat) with a 1/8 inch (3 mm) skin thickness at the trailing edge and a 3/4 inch (19 mm) thickness at the leading edge. However, the rocket motor was unsatisfactory and the aircraft was fitted with two Westinghouse 19-B (J30) turbojets instead. This lead to changing the name to XP-79B. After the failure of the rocket motor, the first two prototypes were cancelled.
Perhaps the most interesting design idea of the XP-79, and the feature which earned it the nickname "Flying Ram" was the reinforced leading edges on the wings. It was envisioned that the XP-79 might actually employ the combat tactic of deliberately colliding with enemy aircraft — perhaps diving into them from above. The idea was that the reinforced XP-79 would slice through the enemy aircraft, perhaps at the wing or tailboom, causing it to crash, but that the XP-79 itself would survive the encounter.
The pilot controlled the XP-79 through a tiller bar and rudders mounted below; intakes mounted at the wingtips supplied air for the unusual bellows-boosted ailerons.[2]
Testing
The XP-79 project (after delays because of bursting tires on taxiing trials on the Muroc Dry Lake) met its own doom on 12 September, 1945 on its maiden flight when after a normal takeoff the single prototype entered an uncontrollable spin 15 minutes into the flight and was lost, killing test pilot Harry Crosby (who was almost killed in a similar crash in the MX-324 two years earlier) when he was unable to bail out safely. Shortly thereafter, the project was cancelled.
Specifications (XP-79B Flying Ram)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 14 ft 0 in (4.27 m)
- Wingspan: 28 ft 0 in (8.54 m)
- Height: 7 ft 0 in (2.13 m)
- Wing area: 278 ft² (25.8 m²)
- Empty weight: 5,840 lb (2,650 kg)
- Loaded weight: 8,669 lb (3,932 kg)
- Powerplant: 2× Westinghouse 19B turbojet, 1,150 lbf (5.1kN) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 547 mph (880 km/h)
- Range: 993 mi (1,598 km)
- Service ceiling: 40,000 ft (12,200 m)
- Rate of climb: 4,000 ft/min (1,220 m/min)
- Wing loading: 31 lb/ft² (153 kg/m²)
- Thrust/weight: 0.27
Armament
- 4 x .50-cal (12.7 mm) machine guns (never fitted)
References
- Winchester, Jim. The World's Worst Aircraft: From Pioneering Failures to Multimillion Dollar Disasters. London: Amber Books Ltd., 2005. ISBN 1-904687-34-2.
External links
Related content
Related development
Comparable aircraft
Designation sequence
XP-76 -
XP-77 -
XP-78 -
XP-79 -
P-80 -
XP-81 -
P-82
Related lists
See also
Fighters: FT · XP-56 · P-61 · F2T · XP-79 · F-89 · F-5 · CF-116 · YF-17 · F-18L · F-20 · YF-23
Attack: YA-13 · XA-16 · A-17 · BT · SBT · YA-9 - Bombers: YB-35 · B2T · YB-49 · B-62 · B-2
Transports: Alpha · C-19 · Beta · C-100 Gamma · RT Delta · YC-125
Reconnaissance: F-15 · RF-5 · TR-3 - Trainers: T-38
Experimental: N-1M · N-9M · MX-324 · X-4 · M2-F2 · M2-F3 · HL-10 · Tacit Blue · X-21
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |