PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
Canadair CF-5
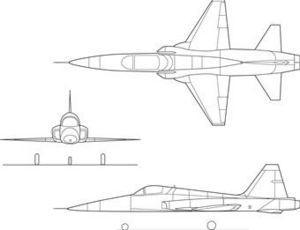
The Canadair CF-5 (officially designated the CF-116 Freedom Fighter) was the Canadair licensed-built version of the American Northrop F-5 Freedom Fighter aircraft primarily for the Canadian Forces. The CF-5 was upgraded periodically throughout its service career in Canada. The Canadian Forces retired the type in 1995, although CF-5s continued to be used by other countries into the early 21st century.
The CF-5 was ordered by the Royal Canadian Air Force, which became part of the Canadian Forces on 1 February 1968. The new unified force took delivery of the first CF-5s (it was almost universally referred to as the CF-5 except in official documentation) at the end of 1968. Total production by Canadair for Canadian Forces was 89 single-seat aircraft and 46 dual-seat aircraft, but many were also built for the Netherlands and Norway as well, some surplus aircraft were sold to Venezuela.
Contents
Design and development
Originally designed by Northrop as a low-cost, low-maintenance fighter jet, the F-5 was intended for use by air forces that had limited resources and technical expertise to maintain a sophisticated aircraft. For Canada, which had an extensive aerospace industry, selection of the F-5 was seen as a step backwards and soon received the derisive RCAF nicknames, "Tinkertoy" or the "Supersonic Tinkertoy."[1] Selected originally to provide a tactical support role based in Canada, the CF-5 was also committed to NATO's northern flank to act a rapid-deployment force. However, the role for the CF-5 throughout its service with the RCAF was changed frequently and eventually, the diminutive fighter would serve as a light attack strike fighter, reconnaissance platform and trainer.
The Canadian version had several modifications to make it more suitable to operating in Canadian Forces theaters. In order to address complaints about long take-off runs, the Canadair version featured a two-position nose landing gear; compressed it operated like the original, but extended (before takeoff) it raised the nose and thereby increased the angle of attack and increased lift. The system reduced takeoff distance by almost 20%. A mid-air refueling probe was installed, Orenda built General Electric J85-15 engines with 4,300 lbf (19 kN) thrust were used, and a more sophisticated navigation system was added. The nose of the CF-5 was also interchangeable with a specially designed reconnaissance set with four cameras in it. Over the course of its life, it received many upgrades to its avionics and capabilities.
Operational history
Initially 433 squadron and 434 squadron were the only two squadrons to operate the CF-5. It was intended that three squadrons would fly the aircraft, but due to budgetary restrictions, the excess aircraft were put into storage in CFB North Bay and CFB Trenton, some later being sold to other countries. 434 squadron was assigned to do lead-in tactical fighter training for the CF-104, but was transitioned to the role of a rapid reaction squadron, being ready to deploy to Europe at a moment's notice in the event of hostilities. The squadron moved to CFB Bagotville with 433 squadron, for a short time, and then on to CFB Chatham.
The training role was adopted by 419 Squadron in CFB Cold Lake; it would continue to provide jet training, dissimilar air combat training (wearing quasi-Soviet "aggressor" paint schemes similar to USAF, USN and USMC F-5Es), and serve as a lead-in fighter trainer for the CF-18 until the aircraft was retired in 1995. All remaining airframes were put into storage at CFB Mountainview.
Variants
- CF-5A : Single-seat fighter version for the Canadian Forces, designation CF-116A. 89 built.
- CF-5A(R) : Single-seat reconnaissance version for the Canadian Forces. Built in small numbers. Canadian Forces designation CF-116A(R).
- CF-5D : Two-seat training version for the Canadian Forces, CF-116D. 46 built.
- NF-5A : Single-seat fighter version for the Royal Netherlands Air Force. 75 built.
- NF-5B : Two-seat training version for the Royal Netherlands Air Force. 30 built.
- VF-5A : Single-seat fighter version for the Venezuelan Air Force.
- VF-5D : Two-seat training version for the Venezuelan Air Force.
Operators

- Netherlands Air Force
- No. 313 Squadron
- No. 314 Squadron
- No. 315 Squadron
- No. 316 Squadron
Aircraft on display
- Defence Research and Development Canada - Toronto (DRDC), Downsview, Ontario
- Canada Aviation Museum, Ottawa, Ontario
- Canadian War Museum Ottawa, Ontario - reconnaissance version
- Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum in Hamilton, Ontario
- Cold Lake Air Force Museum
- CFB Cold Lake - on the approach road mounted in a climbing position
- CFB Winnipeg - Air Force Heritage Park
- Holiday Inn hotel, Trenton, Ontario - mounted by its tailpipes in a steep climb and visible from Ontario Highway 401
- Kamloops Airport
- National Air Force Museum of Canada, Trenton, Ontario
- Worthington Museum at CFB Borden, Ontario
- Toronto/Markham Airport at Markham, OntarioTemplate:Citation needed
Specifications (CF-116)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1-2
- Length: 47 ft 2 in (14.38 m)
- Wingspan: 25 ft 10 in (7.87 m)
- Height: 13 ft 2 in (4.01 m)
- Wing area: 186 ft² (17.28 m²)
- Empty weight: 8,681 lb (3,938 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 20,390 lb (9,249 kg)
- Powerplant: 2× Orenda-built GE J85-15 turbojet
- Dry thrust: 2,925 lbf (13.0 kN) each
- Thrust with afterburner: 4,300 lbf (19.1 kN) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,575 km/h (978 mph [2])
- Range: 760 nmi (660 mi, 1,400 km)
- Service ceiling: 41,000 ft (12,000 m)
- Rate of climb: 34,400 ft/min (10,500 m/min)
Armament
- Guns: 2× 20 mm (0.787 in) Pontiac M39A2 cannons in the nose, 280 rounds/gun
- Rockets: 2× CRV7 rocket pods
Or 2× LAU-10 rocket pods with 4× Zuni 127 mm rockets each
Or 2× Matra rocket pods with 18× SNEB 68 mm rockets each - Missiles: 2× AIM-9 Sidewinder Air-to-air missiles
- Bombs: 7,000 lb (3,200 kg) of payload on five external hardpoints, including a variety of air-to-ground ordnance such as the AGM-65 Maverick air-to-surface missiles, Mark 80 series of unguided iron bombs (including 3 kg and 14 kg practice bombs), CBU-24/49/52/58 cluster bomb munitions, M129 Leaflet bomb and drop tanks for extended range
Badges
- CF5Crest.jpg
CF-5 crest worn by Canadian Forces aircrew and ground crew in the mid-1970s
See also
Related development
Comparable aircraft
Related lists
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |
References
Notes
Bibliography
- McIntyre, Bob. Canadair CF-5 (Canadian Profile: Aircraft No. 4). Ottawa, Ontario: Sabre Model Supplies Ltd., 1985. ISBN 0-920375-02-2.
- Pickler, Ron and Larry Milberry. Canadair: the First 50 Years. Toronto: CANAV Books, 1995. ISBN 0-921022-07-7.
- Stachiw, Anthony L. Canadair CF-5 Freedom Fighter (Canadian Service Aircraft No.1). St. Catharine's, Ontario: Vanwell Publishing, 2003. ISBN 1-55125-073-X.
External links
- RCAF.com: The History and Heritage of Canada's Aircraft
- Atlantic Canada Aviation Museum: Canadair CF-5 Freedom Fighter
Fighters: FT · XP-56 · P-61 · F2T · XP-79 · F-89 · F-5 · CF-116 · YF-17 · F-18L · F-20 · YF-23
Attack: YA-13 · XA-16 · A-17 · BT · SBT · YA-9 - Bombers: YB-35 · B2T · YB-49 · B-62 · B-2
Transports: Alpha · C-19 · Beta · C-100 Gamma · RT Delta · YC-125
Reconnaissance: F-15 · RF-5 · TR-3 - Trainers: T-38
Experimental: N-1M · N-9M · MX-324 · X-4 · M2-F2 · M2-F3 · HL-10 · Tacit Blue · X-21
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |
ms:Canadair CF-5 no:Canadair CF-5 Freedom Fighter ru:Canadair CF-5 vi:Canadair CF-5
| This article is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License. It uses material from the Wikipedia article "Canadair CF-5". |