PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
Ilyushin Il-96
| Ilyushin Il-96 | |
|---|---|
| Aeroflot Il-96-300 | |
| Type | Widebody airliner |
| Manufacturer | Ilyushin |
| Maiden flight | September 28, 1988 |
| Introduced | December 29, 1992 with Aeroflot |
| Primary users | Aeroflot Domodedovo, Cubana |
| Produced | 1993- |
| Number built | 17 |
The Ilyushin Il-96 is a four-engined long-range widebody airliner, which incorporates advanced achievements in Russian and foreign aerospace technology. The IL-96-300 aircraft is designed by Ilyushin Aviation Complex in the city of Moscow, Russia, and it's manufactured by Voronezh Aircraft Manufacturing Company in Voronezh, Russia. The aircraft is powered by four turbofan two-shaft Aviadvigatel PS-90 engines, produced by Perm Motors in Perm, Russia.
Contents
Overview

The Ilyushin Il-96 is a shortened, long-range, and advanced technology development of Russia's first widebody airliner, the Ilyushin Il-86. It features supercritical wings fitted with winglets, a glass cockpit, and a fly-by-wire control system. It was first flown in 1988 and certificated in 1992. The IL-96-300 aircraft equipped with modern Russian made avionics which includes six multifunctional color-LCD displays, electro remote management system, inertial navigation system, collision air avoidance system (including mode “S”) and satellite navigation equipment, VHF communication with grid of 8,33/25 kHz frequencies, and equipment permitting executes flights in RVSM conditions. It allows operating the airplane with two crew members. The avionics correspond to modern requirements on international routes in Europe and North America (RNP-1) and allows to navigate and land under ICAO CAT IIIA conditions. The Il-96 comes in three main variants: the Il-96-300, Il-96M/T and Il-96-400.
The Il-96-300 has a passenger cabin layout for 262 seats, 18 seats with pitch equal to 54 inches plus 244 seats with pitch equal to 32 inches. Galleys are positioned on the upper deck, 18 containers LD-3 and crew rest room are positioned on the lower deck. There is also stipulated a converting of this layout to the 289 seats layout by changing seats in the business class section from 18 to 44 with seats pitch of 34". Although its list price is more than 30% lower than the equivalent western types, Russian airlines are not particularly eager to buy it. As of September 2006, there are only 16 Il-96-300s in operation with Aeroflot (6 of the 17), KrasAir (2), Domodedovo Airlines (3; actually operated by Krasair on behalf of AiRUnion alliance), Atlant-Soyuz Airlines (1; cargo version), Cubana de Aviacion (2) and President Putin's airwing (2). Two more aircraft are being readied at the plant in Voronezh for shipment to the government of Cuba. Both Aeroflot and Transaero received tax exemption when importing Western-built aircraft in exchange for their promising to buy a few Il-96's each.
Meanwhile, Air Zimbabwe was planning to purchase 5 Il-96-300, making the airline the largest carrier of the type outside Russia and second largest carrier to operate the planes after Aeroflot. [citation needed] However, after talks with Russian authorities, the order was cancelled (along with Tupolev orders).
In June 2006, Syrianair announced an agreement to purchase two Il-96-400 aircraft and an Il-96-300 aircraft.
The Cuban official newspaper Granma announced on 3 January 2006 the first official flight of the first Cubana IL-96-300, from Havana, Cuba to Buenos Aires, Argentina[1].
It was announced that since the second quarter of 2007 the factory will be tuned to produce only two latest modifications of the plane.
Variants
There are two variants of the Il-96 and launched on two separate occasions. The Il-96-300 was launched in 1985 with introduction into service in 1993. The Il-96M was launched in 1993 with introduction into service in 2000.
Il-96-300
The Il-96-300 is the initial variant and is fitted with Aviadvigatel (Soloviev) PS90A turbofans with a thrust rating of 16,000 kgf (157 kN, 35,300 lbf). Development started in mid-80s while first prototype flew on 28 September 1988, with Russian certification was obtained on 29 December 1992. The first Il-96 entered service with Aeroflot in 1993.
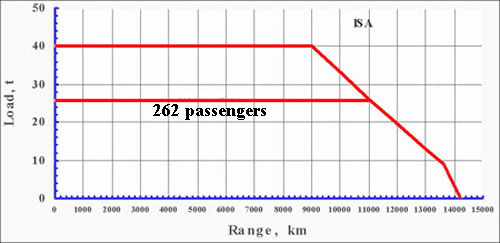
Range with 262 passengers and fuel reserve (for holding during 75 minutes at the altitude 450 m) in a two-class configuration is about 5,940 nautical miles (11,000 km), allowing flights from Moscow to US west coast cities, a far improvement over the Ilyushin Il-86. It is used by Russian president Vladimir Putin as a VIP plane.
This version also comes in a longer range version budded Il-96-300V.
Il-96M
This is a stretched variant of the Il-96-300. It features a 10 m (30 ft) fuselage stretch, is 15 tonnes (33,000 lb) heavier, is fitted with Western-style avionics, and is powered by four Pratt & Whitney PW2337 engines with a thrust rating of 37,000 lbf (165 kN). Range with 312 passengers in a three-class configuration or 92 tonne (203,000 lb) payload is about 5,600 nautical miles (10,400 km). This turned it into a true—but vastly more capable—Il-86 successor. The Il-96M/T is broadly comparable with the Airbus A330-300 and Boeing 777-200A, but is much cheaper. Development on the M/T variant stalled when the US Export-Import Bank suspended talks on financing the engines and avionics, due to Russia's economic problems [2]. This version is also used as President Putin's VIP transport plane. The Il-96M also dispenses the need for a flight engineer. It is designed for a crew of two.
Il-96T
This is the freighter version of the Il-96M.
Il-96-400
The Il-96-400 was developed with Russian avionics and engines. It is based on the Il-96M/T fuselage and is powered by four Aviadvigatel PS90-A1 turbofans. It can carry up to 435 passengers. Typical two-class configuration will have 332-340 passengers. Range with 247 passengers in a three-class configuration is about 11,300 km.
Specifications
| Measurement | Il-96-300 | Il-96-M | Il-96T |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length | 55.3 m or 181 ft 7 in | 64.7 m or 212 ft 3 in | 63.9 m or 209 ft 9 in |
| Span | 60.11 m or 197 ft 3 in | ||
| Height | 17.5 m or 57 ft 7 in | ||
| Zero Fuel Weight | 183,000 kg or 403,000 lbs | ||
| Maximum take-off weight | 250,000 kg (551,000 lb) | 270,000 kg (595,000 lb) | |
| Cruising speed | .80 Mach | ||
| Maximum speed | .82 Mach | ||
| Range fully loaded | 11,482 km or 6,195 nm | 9,700 km or 5,237 nm | |
| Max. fuel capacity | 150,000 liters 39,625 USG | ||
| Engines (example) | Aviadvigatel PS-90A | Pratt & Whitney PW2000 | |
| Cockpit crew | Three | Two | |
| 3-class Seating | 259 | 307 | |
IL-96-300 Payload-range
Aircraft life time
| IL-96-300/-400 aircraft life time | |
|---|---|
| Years | 20 |
| Landings | 20000 |
| Flying hours | 60000 |
Avionics
On the airplane are installed the following systems providing ICAO recommendations and Eurocontrol requirements:
- Integrated control panel of communication and navigation KPRTS-95М-1 and Flight management system VSS-95-1V
- Upgraded Electronic Indication systems SEI-85М and KISS-1-2МA (redaction 6) with LCD indicators
- Inertial system NSI-2000MT or BINS-85
- Ground approximation system EGPWS with the terrain relief information or SRPBZ (or MARK V)
- Collision air avoidance system CAS-81A (or SPS-2000)
- System BRIK-324
- Domestic system of selective calling of crew on radio communication (Selcal) – АSV-324
- Weather locator Buran-А, or MN RLS – without wind shear (or RDR-4B with functions of wind shear warning and turbulence detection)
- MV-range radio station «Orlan-85STD» with maintenance of VDL Mode 2
- Crew satellite communication system Aero Mini M or Aero I (telephone and data exchange with UVD and airline)
- Sound information solid-state registrar RZBN-1, ensuring crew members negotiation recording and cabin sound situation (4 channels) with record conservation of 2 hours of flight information
- System MSRP-A-02 with solid-state protected and operational storage devices
Il-96 Deliveries
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 | 1999 | 1998 | 1997 | 1996 | 1995 | 1994 | 1993 | 1992 | 1991 |
| 2 | 0 |
Incidents
- Following a series of incidents, one of which involved President Putin's jet in Turku, Finland, Russian civil aviation authorities grounded all the Ilyushin-96-300's from 22 August to 3 October 2005 to examine the braking gear.
Trivia
- The Il-96 is the second Russian airplane after the Tu-204 to feature western engines, the Pratt & Whitney PW2000, powering the Il-96M. However, a lack of financing from the US Export-Import Bank caused the program to be cancelled.
Internal and External Links
Related content
Comparable aircraft
Airbus A330 - Boeing 767-300 - Boeing 777-200
Related lists
Fighters: Il-1 - Attack: Il-2 · Il-8 · Il-10 · Il-16 · Il-40 · Il-102
Bombers: Il-4 · Il-6 · Il-20 (I) · Il-22 (I) · Il-28 · Il-30 · Il-46 · Il-54
Transports: Il-12 · Il-14 · Il-18 · Il-20 (II) · Il-32 · Il-34 · Il-62 · Il-76 · Il-78 · Il-80 · Il-86 · Il-96 · Il-106 · Il-114
Reconnaissance: Il-20 (III) · Il-22 (II) · Il-24 · Il-38 · A-50 - Trainers: Il-103
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |
bg:Ил-96 de:Iljuschin Il-96 et:Iljušin Il-96 fr:Iliouchine Il-96 id:Ilyushin Il-96 hu:Il–96 nl:Iljoesjin Il-96 ja:Il-96 (航空機) no:Iljusjin Il-96 ru:Ил-96 sr:Иљушин 96 fi:Iljušin Il-96 sv:Iljusjin Il-96 vi:Il-96 zh:伊尔96