PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
Ilyushin Il-76
| Ilyushin Il-76 | |
|---|---|
| IL-76 landing at Balad Air Base in 2005 | |
| Type | Strategic airlifter |
| Manufacturer | Ilyushin |
| Designed by | Ilyushin |
| Maiden flight | March 25 1971 |
| Introduced | June |
| Status | Operational |
| Primary user | Russian Air Force |
| Produced | IL-76: |
| Number built | 960 |
| Variants | Ilyushin Il-78 Beriev A-50 |
The Ilyushin IL-76 (NATO reporting name: Candid) is a 4-engined strategic airlifter designed in the Soviet Union and in widespread use in eastern Europe, Asia and Africa.
Contents
History
The aircraft was first conceived by Ilyushin in 1967 to meet a requirement for a freighter able to carry a payload of 40 tons (88,000 lb) over a range of 5,000 km (2,700 nautical miles (3,100 statute miles;) in less than six hours, able to operate from short and unprepared airstrips, and capable of coping with the worst weather conditions likely to be experienced in Siberia and the Soviet Union's Arctic regions. The basic layout of the plane was similar to the U.S.-built Lockheed C-141 Starlifter, but the new design had a larger cargo hold area and more powerful engines to achieve the desired performance. It first flew on March 25, 1971, and is still in production in Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
According to Venik's Aviation pages online, in 2000, FEMA requested two Il-76 waterbombers to respond to Los Alamos area wildfires. Venik further reported this order was countermanded by the U.S. Forest Service.
On August 29, 2005, the day before the levees of New Orleans gave way to the forces of Hurricane Katrina, the Russian Federation offered humanitarian aid to the United States. Two (2) EMERCOM IL-76 aircraft landed at a disaster aid staging area at Little Rock, Arkansas September 8. This marks the first time Russia has flown such a mission to North America. A second Emergency Situations ministry IL-76 first-aid shipment, specially arranged with the U.S. leadership, departed Russia for Little Rock September 14.
India also used an IL-76 to deliver aid on September 13, 2005 for Katrina victims.
The Il-76 is also in use as an airborne tanker, otherwise known as a refueller (Il-78), and a waterbomber. Its airframe was used as a base for the Beriev A-50 'Mainstay' AWACS aircraft.
The U.S. Air Force gave the Il-76 the nickname "141-ski", due to the fact that it looks is similar to Lockheed C-141 Starlifter. Il-76TD, TF and D are employed by U.S. Government worldwide.[citation needed]
Incidents and accidents
Description
Specifications (Il-76D)
General characteristics
- Crew: 5
- Capacity: 40,000 kg (IL-76), 48,000 kg (IL-76M/T), 50,000 kg IL-76MD/TD), 60,000 kg (IL-76MF/TF)
- Length: 46.59 m (152 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 50.5 m (165 ft 8 in)
- Height: 14.76 m (48 ft 5 in)
- Wing area: 300.0 m² (3,229.2 ft²)
- Empty weight: 72,000 kg (IL-76), 92,000 kg (IL-76MD/TD), 104,000 kg (IL-76MF/TF) (159,000 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 157,000 kg (IL-76), 170,000 kg (IL-76M/T), 190,000 kg IL-76MD/TD), 210,000 kg (IL-76MF/TF) (346,000 lb (IL-76))
- Powerplant: 4× Soloviev D-30KP turbofans, 118 kN (26,500 lbf)) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 900 km/h (490 kt, 560 mph)
- Range: (with max payload) 3,650 km (IL-76), 4,000 km (IL-76M/T), 4,400 km (IL-76MD/TD), 4,200 km (IL-76MF/TF) (nm, mi)
- Service ceiling: 13,000 m (42,700 ft)
- Rate of climb: m/s (ft/min)
- Wing loading: 566.7 kg/m² (IL-76M/T), 633.3 kg/m² (IL-76MD/TD) (116.05 lb/ft² (IL-76M/T), 129.72 lb/ft² (IL-76MD/TD))
- Thrust/weight:
- minimal landing run: 450 m (with thrust reversal)
Armament
- Guns: 2× 23 mm cannon in radar-directed manned turret at base of tail
Some military models have 2 hardpoints under each outer wing capable of supporting 500 kg bombs.
Military variants
- Il-76D ('D' for Desantniy, Десантный - "for paratroopers") has a gun turret in the tail for defense purposes.
- Il-76M - Transport version.
- Il-76MD - Transport version.
- Il-76MF - Stretched military version.
- Il-76PP - Il-76MD-based radio jammer
- SKIP (СКИП - Самолетный Контрольно-Измерительный Пункт, Airborne Check-Measure-and-Control Point) - Il-76/A-50 based aircraft initially built to support Kh-55 cruise missile tests.
Civil variants
- Il-76T - ('T' for Transport, Транспортный) unarmed civil cargo transport version. NATO code-name Candid-A. It first flew on November 4, 1978.
- Il-76TD - The civil equivalent of the Il-76MD, first flew in 1982.
- Il-76TF - Civil transport stretched version with Aviadvigatel PS-90 engines. It is the civil version of the Il-76MF
- Il-76P - Firefighting aircraft. The Il-76 waterbomber is a VAP-2 1.5 hour install/removal tanking kit conversion. The Il-76 can carry 11,000 U.S. gallons (41,600 liters) of water; three times the capacity of the C-130 Hercules. Since this kit can be installed on any Il-76, the designation Il-76TP, Il-76TDP are also used when those versions of the Il-76 are converted into waterbombers. The Il-76P was first unveiled in 1990
Foreign Variants
Foreign operators of Il-76 has adopted the airframe as the base their own AWACS and other modifications, and these included:
KJ-2000
Domestic Chinese AWACS conversion of Il-76 after the setback of the A-50I.
The current KJ-2000 AWACS in Chinese service is equipped with a domestic Active Electronically Scanned Array active phased array radar system similar to the Swedish Ericsson's Erieye radar. The radar is designed by the Research Institute of Electronic Technology (also more commonly known as the 14th Institute) at Nanjing, and it utilizes the experience gained from the 14th Institute's earlier indigenously developed Type H/LJG-346 SAPARS (Shipborne Active Phased Array Radar System) that was completed in 1998 (the same Type H/LJG-346 SAPARS was also the predecessor of the active phased array radar system onboard PLAN Lanzhou class destroyer). Chinese claim that the domestic radar is superior to the Israeli radar and it can track more targets at greater range. The radar is arranged in the same way as that of A-50I.
CFTE Engine Testbed
China Flight Test Establishment (CFTE) currently operates a flying testbed converted from a Russian-made Il-76MD jet transport aircraft to serve as a flying testbed for future engine development programmes. The first engine to be tested on the aircraft is the WS-10A “Taihang” turbofan, currently being developed as the powerplant for China’s indigenous J-10 and J-11 fighter aircraft. The #76456 Il-76MD, acquired by the AVIC 1 from Russia in the 1990s, is currently based at CFTE’s flight test facility at Yanliang, Shaanxi Province.
Adnan I
Iraqi development (with French assistance) with fibreglass-reinforced plastic radome over the antenna of the Thomson-CSF Tiger G surveillance radar with a maximum detection range of 189 nm (217.5 miles; 350 km). Nonoperational after the Gulf War.
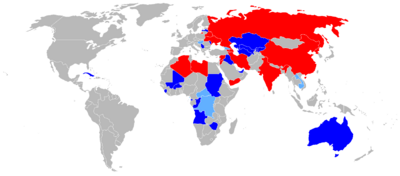
Operators
Both military and civil operators in 38 countries have operated 850+ Il-76 in large numbers. In the list below, known current operators are listed in bold.
- Template:DZA
- The Algerian Air Force operates 17 Il-76 aircraft, including 3 Il-76MD, 8 Il-76TD, and 6 Il-78.
- Template:ANG
- Gira Globo operates 1 Il-76[1].
- Template:ARM
- The Armenian Air Force operates 2 Il-76 aircraft.
- Dvin Airlines has operated an Il-76TD.
- Yerevan-Avia operates 1 Il-76.
- Template:AUS
- Adagold Aviation operates a single Il-76T[2].
- HeavyLift Cargo Airlines has chartered Il-76 aircraft but does not currently operate the aircraft.
- Template:AZE
- The Azerbaijan Air Force operates 3 Il-76 aircraft.
- Azal Avia Cargo operates 1 Il-76TD.
- Azerbaijan Airlines operates 1 Il-76M.
- Silk Way Airlines operates 8, including 1 Il-76MD and 7 Il-76TD.
- Template:BLR
- The Belarusian Air Force inherited a number of Il-76 aircraft from the Soviet Air Force.
- Belair operated the Il-76 before its closure in 1999.
- Transaviaexport Cargo Airline operates 23, including 5 Il-76MD and 18 Il-76TD.
- Template:BFA
- Faso Airways operates a single Il-76TD.
- Template:CAF
- Template:CAM
- Imtrec Aviation has operated a Laotian registered Il-76.
- Template:CHN
- The People's Liberation Army Air Force operates 17 Il-76 aircraft, including 3 KJ-2000 AWACS versions and some Il-78 tankers, with a further 30 due for delivery.
- China United Airlines has operated the Il-76, but does not currently.
- Template:Country data Republic of the Congo
- The Republic of the Congo operates an Il-76.
- Template:CUB
- Cubana de Aviación operates 1 Il-76MD.
- Template:COD
- Template:EQG
- Ecuatorial Cargo operates 1 Il-76TD[4].
- Express International Cargo
- Template:HUN
- Atlant Hungary has operated the Il-76[5].
- Hungarian Ukrainian Air Cargo has operated the Il-76[6]
- Template:IND
- The Indian Air Force operates 24 Il-76MD and 6 Il-78MKI aircraft.
- Template:IRN
- The Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force operates the Il-76.
- The Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps operates the Il-76, including some modified to carry AWACS radar.
- Atlas Air has operated at least 8 Il-76TD[7].
- Chabahar Air has operated at least 2 Il-76TD[8].
- Mahan Air has operated the Il-76.
- Payam Air operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Qeshm Air operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Safiran Airlines is a former operator.
- Template:IRQ
- The Iraqi Air Force operated the Il-76, but none remain in service.
- Iraqi Airways operates a single Il-76.
- Template:JOR
- The Royal Jordanian Air Force operates 2 Il-76 aircraft.
- Template:KAZ
- The Government of Kazakhstan operates 1 Il-76.
- Air Almaty operates an Il-76TD for leased operations[9].
- Air Kazakhstan operated Il-76 aircraft until its closure in 2004.
- GST Aero operates 1 Il-76T[10].
- Kazakhstan Airlines operated the Il-76TD before its closure in 1997.
- Sayakhat Airlines operated the Il-76 previously.
- Template:KGZ
- Botir Avia operates 3, including 1 Il-76MD and 2 Il-76TD.
- Kyrgyzstan Airlines operates 1 Il-76TD.
- Reem Air
- Template:LAT
- Inversija operates 3, including 2 Il-76T and 1 Il-76TD.
- Template:LBA
- The Libyan Air Force has operated the Il-76 although it may not remain in service.
- Buraq Air operates 6, including 3 Il-76MD and 3 Il-76TD.
- Jamahiria Air Transport operates the Il-76M, Il-76TD, and Il-78[11].
- Libyan Air Cargo, the cargo division of Libyan Arab Airlines, operates 21, including 1 Il-76M and 15 Il-76TD.
- Tobruk Air
- Template:MLI
- Template:MOL
- Aerocom operated an Il-76MD as well as an Il-76T until as late as January 2005.
- Airline Transport operated a number of Il-76 aircraft, losing 3 in accidents in 2004 and 2005.
- Jet Line International operates the Il-76[12]
- Tiramavia
- Template:NKO
- Template:RUS
- The Russian Air Force inherited large numbers of the aircraft from the Soviet Air Force in 1991, and many remain in service.
- The Ministry of Extraordinary Situations operates an Il-76TD.
- Abakan Avia operates 3 Il-76TD.
- Aeroflot operated large numbers of aircraft, especially during Soviet years, often on behalf of the Soviet military. However, none remain in service with the airline.
- Air STAN operated an Il-76TD[13].
- Airlines 400 operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Airstars Airways operates 4 Il-76TD on cargo services.
- ALAK operated Il-76 aircraft before its closure in 1999.
- Alrosa Avia operates 4 Il-76TD on charter services.
- Aram Air
- Atlant-Soyuz Airlines operates 6, including 2 Il-76MD and 4 Il-76TD.
- ATRAN Cargo Airlines operates 5, including 3 Il-76T and 2 Il-76TD. At least one Il-76M may have been operated in the past.
- Atruvera Aviation operates 3, including 1 Il-76MD and 2 Il-76TD.
- Aviacon Zitotrans operates 5, including 4 Il-76TD.
- Aviaenergo operated the aircraft, but none remain in service.
- Aviast operates 4, including 1 Il-76MD and 3 Il-76TD.
- Continental Airways has operated the Il-76 in the past, but does not do so currently.
- Dacono Air has operated the Il-76.
- Dobrolet Airlines operates 3 Il-76TD.
- Domededovo Airlines has operated the Il-76, but none are currently in service.
- East Line operates the Il-76.
- Emercom operates the Il-76TD[14]
- Ilavia Airline operates 6, including 2 Il-76MD and 4 Il-76TD.
- KrasAir operated the Il-76, but none are currently in service.
- Krylo Airlines operated 2 Il-76TD into 2005.
- Magadan Avia Leasing is a lease and charter operator of the Il-76.
- Moscow Airways operated an Il-76TD in the early 1990s[15].
- Novosibirsk Air Enterprise operated the Il-76, but none are currently in service.
- Pulkovo Aviation Enterprise operated the Il-76, but none are currently in service.
- Samara Airlines operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Tesis Aviation Enterprise operates 9 Il-76TD.
- Tyumen Airlines
- Uralinteravia
- Volga-Dnepr operates 7 Il-76TD.
- Template:SER
- Air Tomisko operates a single Il-76TD.
- Kosmas Air operates a single Il-76TD.
- Template:SLE
- Template:USSR
- The Soviet Air Force operated hundreds of the aircraft, with an inventory of 310 in 1987. Most were dispersed to the successor states upon the breakup of the Soviet Union.
- Aeroflot was the main civil user of the aircraft during the period of the Soviet Union, although many of its aircraft were operated on behalf of the military.
- Jet Air Cargo was one of the first civil operators of the Il-76 in Russia other than Aeroflot[17].
- Template:SUD
- Air West operated a small number of aircraft, although it is unclear how many remain in service.
- Azza Transport operates 2 Il-76TD.
- East West Cargo operated a number of Il-76 aircraft.
- Juba Cargo operates the Il-76[18]
- Sarit Air Lines operates 1 Il-76, now as part of Badr Airlines.
- Trans Attico
- Template:SYR
- The Syrian Air Force operates the Il-76.
- Syrian Arab Airlines operates 4, including 3 Il-76M.
- Template:TKM
- Turkmenistan Airlines operates 8 Il-76TD.
- Template:UKR
- The Ukrainian Air Force inherited a large number of Il-76 aircraft from the Soviet Air Force, with as many as 100 remaining in service.
- Air Service Ukraine operated the Il-76MD.
- Air Ukraine and Air Ukraine Cargo operated the aircraft, although none were in service at the time of bankruptcy.
- ATI Aircompany operates a number of Il-76 models.
- Azov Avia Airlines operates 2 Il-76MD.
- BSL Airline operated as many as 6 Il-78[19].
- Busol Airlines operated the Il-76 before its closure in 1998.
- Khors Aircompany operates 2 Il-76MD.
- Lviv Airlines operates 3 Il-76MD.
- South Airlines is a former operator.
- Ukraine Air Alliance operates 4, including 1 Il-76MD and 3 Il-76TD.
- Ukrainian Cargo Airways operates 21, including 19 Il-76MD.
- Veteran Airlines
- Volare Airlines operates 3, including 2 Il-76MD and 1 Il-76TD.
- Yuzmashavia operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Template:UAE
- Gulf Aviation Technology and Services operates a number of Il-76 aircraft on charter or lease.
- Phoenix Aviation operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Template:UZB
- Avialeasing operates the Il-76 on a charter and lease basis.
- Uzbekistan Airways operates 14 Il-76TD.
- Template:YEM
- The Yemen Air Force operates 3 Il-76 aircraft.
- Yemenia operates 2 Il-76TD.
- Template:ZIM
- Avient Aviation operates 1 Il-76.
References
- ↑ "Ilyushin Il-76 D2-FEM", AirTeamImages.com.
- ↑ "Ilyushin IL76", Adagold Aviation Pty Limited
- ↑ "Air Congo Ilyushin Il-76", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Ecuatorial Cargo Ilyushin Il-76TD", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Atlant-Hungary Ilyushin Il-76TD", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "HUK - Hungarian Ukrainian Air Cargo Ilyushin Il-76TD", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Atlas Air Ilyushin Il-76TD", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Chabahar Air Ilyushin Il-76TD", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Lease", Air Almaty
- ↑ "GST Aero Ilyushin Il-76T", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Jamahiria Air Transport Ilyushin Il-76/78", Airliners.net.
- ↑ Jet Line
- ↑ "Air STAN Ilyushin Il-76", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Emercom Ilyushin Il-76", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Moscow Airways Ilyushin Il-76", Airliners.net.
- ↑ "Ilyushin 76", Aerolift
- ↑ "Jet Air Cargo Ilyushin Il-76TD", Airliners.net.
- ↑ JUBA Cargo
- ↑ "BSL Airline Ilyushin Il-78", Airliners.net.
See also
Related development
Comparable aircraft
Related lists
Fighters: Il-1 - Attack: Il-2 · Il-8 · Il-10 · Il-16 · Il-40 · Il-102
Bombers: Il-4 · Il-6 · Il-20 (I) · Il-22 (I) · Il-28 · Il-30 · Il-46 · Il-54
Transports: Il-12 · Il-14 · Il-18 · Il-20 (II) · Il-32 · Il-34 · Il-62 · Il-76 · Il-78 · Il-80 · Il-86 · Il-96 · Il-106 · Il-114
Reconnaissance: Il-20 (III) · Il-22 (II) · Il-24 · Il-38 · A-50 - Trainers: Il-103
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |
de:Iljuschin Il-76 el:Il-76 fa:ایلیوشین-۷۶ fr:Iliouchine Il-76 Candid hr:Iljušin Il-76 it:Ilyushin Il-76 he:איליושין Il-76 nl:Iljoesjin Il-76 ja:Il-76 (航空機) ru:Ил-76 sr:Иљушин Ил-76 fi:Iljušin Il-76 vi:Il-76 th:อิลยูชิน อิล-76