PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
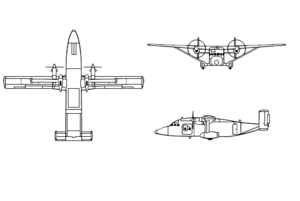
C-23 Sherpa
| C-23 Sherpa | |
|---|---|
| A C-23A Sherpa over West Germany in 1988 | |
| Type | transport aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Bombardier Aerospace |
| Designed by | Short Brothers |
| Maiden flight | December 23 1982 |
| Introduced | 1985 |
| Primary users | United States Army United States Air Force |
| Developed from | Short 330 |
| Variants | Short 360 |
The Short C-23 Sherpa is a small transport aircraft built by Short Brothers. The C-23A and C-23B variants was based on the Short 330. The Short 360 derivative was modified to become C-23B+ and C-23C variants.
Contents
Design and Development
The Short 330 was developed by Short Brothers of Belfast from Short's earlier Short Skyvan STOL utility transport. The 330 had a longer wingspan and fuselage than the Skyvan, while retaining the Skyvan's square shaped fuselage cross section, allowing it to carry up to 30 passengers while retaining good short field characteristics.[1] The 330 entered commercial service in 1976.
In addition to the passenger aircraft, the Shorts also planned two freight versions. The first of these, the Short 330-UTT (for Utility Tactical Transport) was a military transport version fitted with a strengthened cabin floor, and paratroop doors,[2] which was sold in small numbers, primarily to Thailand, who purchased four. The Short Sherpa was a freighter fitted with a full width rear cargo door/ramp. This version first flew on 23 December 1982,[2] with the first order, for 18 aircraft, being placed by the United States Air Force in March 1983, for the European Distribution System Aircraft (EDSA) role, to fly spare parts between USAF air bases within Europe.[2]
In U.S. military service, the Short 330 was designated the C-23A Sherpa. The C-23B Sherpa was similar to the C-23A, but with cabin windows.[3] The Short 360 derivative was modified by replacing the rear fuselage of the Shorts 360, with its single tall fin, with the twin tail and rear loading ramp of the Short Sherpa. The modified Short 360 was designated C-23B+ and C-23C.
The C-23 was produced at the Short Brothers' facility in Belfast, Northern Ireland for the U.S. Dept. of Defense and the Royal Air Force.[4]
Operational history
The C-23A Sherpa entered USAF service in 1985[4] and continuing in use in the EDSA role until 1990, when the EDSA role was disbanded. Six aircraft were passed to the United States Army, where they were used to support the Army National Guard, joining 10 new build C-23B Sherpa aircraft.[3] Other variants are C-23B+ and C-23C. The C-23 replaced the UV-18 Twin Otter in U.S. service. The C-23 is the only cargo plane operated by the U.S Army.[4]
During Iraq War, 2003-present, the C-23 has served the Army's intra-theater needs of cargo and personnel transport. It provides an economic alternative for transporting some 20 people or 3 pallets of cargo when speed is not critical.[5]
On 13 June 2007, the Alenia C-27J was selected to replace the C-23 in US Army service.[6][7]
Variants
- Short 330-UTT
- C-23A Sherpa
- C-23B Sherpa
- C-23B+/C Super Sherpa
Operators
Specifications
C-23A
Data from Jane's All the World's Aircraft, 1988-1989[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: Three (Two pilots plus one cabin crew)
- Capacity: 30 passengers
- Length: 58 ft 0 in (17.69 m)
- Wingspan: 74 ft 9 in (22.78 m)
- Height: 16 ft 3 in (4.95 m)
- Wing area: 453 ft² (42.1 m²)
- Airfoil: NACA 63 series, modified
- Empty weight: 14,200 lb (6,440 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 22,900 lb (10,387 kg)
- Powerplant: 2× Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-45-R turboprops, 1,198 hp (894 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 218 mph (190 knots, 352 km/h) (at 10,000 ft, 3,050 m)
- Cruise speed: 184 mph (160 kt, 296 km/h)
- Stall speed: 85 mph (73 kt, 136 km/h) (flaps and landing gear down)
- Range: 770 mi (915 nm, 1,239 km) (no reserves, passenger version, 1,966 kg payload)
- Service ceiling: 11,500 ft (3,500 m)
- Rate of climb: 2,100 ft/min (60 m/s)
- Wing loading: 50.6 lb/ft² (247 kg/m²)
- Power/mass: 0.052 hp/lb (0.17 kW/kg)
C-23B/C
Data from U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947[8]
General characteristics
- Crew: Three (Two pilots plus one cabin crew)
- Capacity: 18-20 passengers
- Length: 58 ft 0 in (17.7 m)
- Wingspan: 74 ft 10 in (22.8 m)
- Height: 16 ft 5 in (5.0 m)
- Wing area: 456 ft² (42.4 m²)
- Airfoil: NACA 63 series, modified
- Empty weight: 16,040 lb (7,276 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 25,600 lb (11,610 kg)
- Powerplant: 2× Pratt & Whitney Canada PT6A-65AR turboprops, 1,424 hp (1,062 kW) each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 276 mph (knots, km/h)
- Cruise speed: 223 mph (240 kt, 444 km/h)
- Range: 1,185 mi (1,030 nm, 1,907 km)
- Service ceiling: 13,950 ft (4,252 m)
References
- ↑ Donald, David (Editor) (1997). The Encyclopedia of World Aircraft. Aerospace Publishing. ISBN 1-85605-375-X.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Taylor, JWR (Editor) (1988). Jane's All the World's Aircraft, 1988-1989. Jane's Information Group. ISBN 0 7106-0867-5.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Donald, David; Lake, John (editors) (1996). Encyclopedia of World Military Aircraft, Single Volume Edition, London: Aerospace Publishing, p384. ISBN 1 874023 95 6.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Olive-Drab C-23 page
- ↑ "C-23: A Small Cargo Plane that Makes a Big Difference", Military.com, February 9, 2004.
- ↑ C-27J Spartan named as Joint Cargo Aircraft. Air Force Link (2007-06-14). Retrieved on 2007-06-17.
- ↑ C-27J tapped for Joint Cargo Aircraft. Air Force Times (2007-06-14). Retrieved on 2007-06-17.
- ↑ Harding, Stephen (1997). U.S. Army Aircraft Since 1947. Atglen, PA, USA: Schiffer Publishing Ltd., 224-226. ISBN 96-69996.
External links
- C-23 Sherpa page on Florida National Guard site
- C-23 page on Global Security.org
- C-23 page on theAviationZone.com
- Short 330 page on Airliners.net
Related content
Related development
Comparable aircraft
See also
Template:US transport aircraft
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |