PlaneSpottingWorld welcomes all new members! Please gives your ideas at the Terminal.
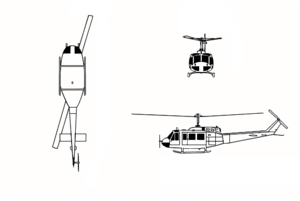
Bell H-1 series
| H-1 series | |
|---|---|
| Bell UH-1D Huey of the United States Army | |
| Type | Multipurpose utility helicopter |
| Manufacturer | Bell Helicopter |
| Maiden flight | October 22, 1956 |
| Primary users | United States Army Japan Ground Self-Defense Force Royal Australian Air Force Philippine Armed Forces |
| Number built | 10,000 |
| Variants | UH-1N Twin Huey AH-1 Cobra Bell 204/205 Bell 212 Bell 214 UH-1Y Venom |
The Bell Helicopter Textron UH-1 Iroquois, commonly (or officially in the United States Marine Corps) known as the "Huey", is a multipurpose military helicopter, famous for its use in the Vietnam War. The "U" stands for utility, in contrast to Attack or Cargo helicopters.
The UH-1 was developed from 1955 US Army trials with the Bell Model 204. The initial designation of HU-1 (helicopter utility) led to its nickname, Huey. It was first used by the military in 1959 and went into triservice production in 1962 as the UH-1. The last were produced in 1976 with more than 16,000 made in total,[1] of which the majority (7,000 or so) were deployed in Vietnam. In Vietnam, 2,202 Huey pilots were killed and approximately 2,500 aircraft were lost, roughly half to combat and the rest to operational accidents.
Contents
Huey/Cobra pics
Development
Earlier helicopters had been powered by piston engines. However, by the early 1950s, turbine engines were being used in many fixed-wing aircraft, and aircraft designers began to consider using them for rotary-wing use. Though expensive to build, turbines were long-lived, durable, and extremely light for their power output in comparison to piston-powered engines.
XH-40
The first Bell helicopter to use a turbine engine was a modified Model 47 (designated the XH-13F), first flown in October 1954. In 1955, anxious to obtain a powerful medical evacuation helicopter, the U.S. Army awarded Bell a contract to develop the next generation turbine-powered helicopter, designated the XH-40 (renamed the Model 204). The first XH-40 flew on October 22, 1956. Two more prototypes were built in 1957, and eighteen more YH-40 prototypes were tested in 1958. Bell believed the YH-40 was ideal for troop transport and cargo carrying as well as the medevac role, a view soon adopted by the Army, who found the pre-production aircraft so much better in service than previous piston-powered helicopters they soon ordered more of them.
The HU-1A (later redesignated the UH-1 Iroquois) was the first turbine-equipped U.S. helicopter to go into production, and production models first entered service with the 101st Airborne at Fort Lewis, Washington. Although they were intended for evaluation only, the Army quickly pressed them into operational service.
The helicopter was originally designated the HU-1A, which is where it received its nickname - "Huey." The official U.S. Army designation Iroquois (Army helicopters are traditionally given Native American names) was almost never used in practice. The HU-1B was equipped with revised main rotor blades and could carry seven passengers. These versions were redesignated UH-1A and UH-1B respectively, in 1962. A UH-1C gunship version with a more powerful engine was later built, along with search and rescue (SAR) and training variants.
Variant overview
U.S. Military variants
- XH-40: The initial Bell 204 prototype. Three prototypes were built.
- YH-40: Six pre-production aircraft.
- Bell Model 533: One YH-40BF rebuilt as a flight test bed with turbofan engines and wings.
- HU-1A: Initial Bell 204 production model, redesignated as the UH-1A in 1962.
- HU-1B: Upgraded HU-1A, various external and rotor improvements. Redesignated UH-1B in 1962.
- UH-1C: UH-1B with improved engine and modified blades and rotor-head for better performance in the gunship role.
- YUH-1D: Seven pre-production prototypes of the UH-1D.
- UH-1D: Initial Bell 205 production model (long fuselage version of the 204). Designed as a troop carrier to replace the CH-34 then in US Army service
- HH-1D: Search Air Rescue (SAR) variant of UH-1D.
- UH-1E: UH-1B/C for USMC with different avionics and equipment. Initial models were also fitted with a retractable rescue hoist.
- TH-1E: Trainer based on the UH-1E for USMC.
- UH-1F: UH-1B/C for USAF with different engine.
- TH-1F: Trainer based on the UH-1F for the USAF.
- AH-1G: The AH-1 Cobra series is technically a member of the H-1 series. For more information consult the main article. On a side note, UH-1D/H gunships operating with the Cambodia armed forces were locally given the designation UH-1G.
- UH-1H: Improved UH-1D with the same engine as the UH-1C, which had actually been developed after the UH-1D.
- CUH-1H: Canadian Forces designation for the UH-1H utility transport helicopter. Redesignated CH-118.
- EH-1H: Twenty-two aircraft converted by installation of AN/ARQ-33 (4 aircraft) and ARQ-33A Radio Receiving Sets. Capable of HF/VHF intercept and VHF jamming. Initial aircraft were fielded to 82nd Airborne and 2nd Armored. The 82nd fielded the type during invasion of Grenada (Operation Urgent Fury) in 1983. Replaced by EH-60A.
- HH-1H: Based off of medical evacuation (MEDEVAC) conversions of the UH-1H, SAR variant to USAF with rescue hoist.
- JUH-1H: Five UH-1Hs converted to SOTAS battlefield surveillance configuration, designed to simulate the Russian Hind.
- TH-1H: Recently modified UH-1H troop carriers for use as basic helicopter flight trainers by the USAF.
- AH-1J: Twin engined version of the AH-1G. Also technically a member of the H-1 series. For more information consult the main article. An improved Japanese version of the UH-1H built under license in Japan by Fuji was also locally given the designation UH-1J.
- HH-1K: Purpose built SAR variant for the US Navy with USN avionics and equipment.
- UH-1L: Utility variant of the HH-1K.
- TH-1L: Helicopter flight trainer based off of the UH-1L for the USN.
- UH-1M: Gunship specific UH-1C upgrade with new engine. Often confused as a dedicated "night-fighter" because the first three UH-1Ms were delivered to the South East Asia Night Operations (SEA NITEOPS) office to be used in the Iroqouis Night Fighter and Night Tracker (INFANT) program.
- UH-1N: Initial Bell 212 production model, the Bell "Twin Pac" twin-engined Huey.
- UH-1P: UH-1F variant for USAF for special operations use including psychological warfare and covert insertion/extraction, and attack operations.
- AH-1Q: Upgraded AH-1G with TOW capability. For more information consult the main article.
- YAH-1R: Upgraded AH-1Q with improved engine. For more information consult the main article.
- AH-1S: Upgraded AH-1Q combined with YAH-1R improvements. For more information consult the main article.
- AH-1T: Upgraded AH-1J. Also technically a member of the H-1 series. For more information consult the main article.
- UH-1U: Single prototype for Counter Mortar/Counter Battery Radar Jamming aircraft. Crashed at Edwards AFB during testing.
- UH-1V: Aeromedical evacuation, rescue version for the US Army.
- AH-1W: Upgraded AH-1T. Also technically a member of the H-1 series. For more information consult the main article.
- EH-1X: Ten aircraft built by ESL. AN/ALQ-151 Mission Equipment. Capable of HF/VHF intercept, VHF Direction Finding/jamming. Replaced by EH-60A
- UH-1Y: Upgraded variant developed from existing upgraded late model UH-1Ns, with additional emphasis on commonality with the AH-1Z.
- AH-1Z: Upgraded AH-1W. Also technically a member of the H-1 series. For more information consult the main article.
Other military variants
- Bell 204: Bell Helicopters company designation, covering aircraft from the XH-40, YH-40 prototypes to the UH-1A, UH-1B, UH-1C, UH-1E, UH-1F, HH-1K, UH-1L, UH-1P and UH-1M production aircraft.
- Agusta-Bell AB 204: Military utility transport helicopter. Built under license in Italy by Agusta.
- Agusta-Bell AB 204AS: Anti-submarine warfare, anti-shipping version of the AB 204 helicopter.
- Fuji-Bell 204B-2: Military utility transport helicopter. Built under licence in Japan by Fuji Heavy Industries. Used by the Japan Ground Self Defence Force under the name Hiyodori.
- Bell 205: Bell Helicopters company designation of the UH-1D and UH-1H helicopters.
- Bell 205A-1: Military utility transport helicopter version, initial version based on the UH-1H.
- Bell 205A-1A: As 205A-1, but with armament hardpoints and military avoinics. Produced specifically for Israeli contract.
- Agusta-Bell 205: Military utility transport helicopter. Built under licence in Italy by Agusta.
- Fuji-Bell 205A-1: Military utility transport helicopter. Built under licence in Japan by Fuji. Used by the Japanese Ground Self Defence Force under the designation HU-1H.[citation needed]
- Bell Huey II: A modified and re-engined UH-1H, significantly upgrading its performance, and its cost-effectiveness. Currently offered by Bell to all current military users of the type.
Specifications (UH-1D)
General characteristics
- Crew: 1-4
- Capacity: 3,880 lb including 14 troops, or 6 stretchers, or equivalent cargo
- Length: 57 ft 1 in with rotors (17.4 m)
- Rotor diameter: 48 ft 0 in (14.6 m)
- Height: 14 ft 5 in (4.4 m)
- Empty weight: 5,215 lb (2,365 kg)
- Loaded weight: 9,040 lb (4,100 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 9,500 lb (4,310 kg)
- Powerplant: 1× Lycoming T53-L-13B turboshaft, 1,400 shp (1,045 kW)
- Maximum speed: 135 mph (220 km/h)
- Cruise speed: 125 mph (205 km/h)
- Range: 315 mi (510 km)
- Service ceiling: 19,390 ft (Dependent on environmental factors such as weight, outside temp., etc) (5,910 m)
- Rate of climb: 1,755 ft/min (8.9 m/s)
- Power/mass: 0.15 hp/lb (0.25 kW/kg)
Variable, but may include a combination of:
- 2x 7.62 mm M60 machine gun, or 2x 7.62 mm GAU-17 machine gun
- 2x 7-round or 19-round 2.75 in (70 mm) rocket pods
For information on US armament systems see:
Popular culture
The image of American troops disembarking from a Huey has become a fixture in depictions of the Vietnam War, and can be seen in practically every movie, video game, and television show on the subject, as well as more modern settings.[citation needed]
Author Robert Mason recounts his career as a UH-1 "Slick" pilot in his memoir, Chickenhawk.
References
- Notes
- ↑ http://www.bellhelicopter.com/en/aircraft/military/bellUH-1Y.cfm Bell Helicopter UH-1 web site
- Bibliography
- Chant, Christopher, Fighting Helicopters of the 20th Century, Graham Beehag Books, Christchurch, Dorset, England (1996).
- Debay, Yves, Combat Helicopters, France: Histoire & Collections (1996)
- Drendel, Lou. UH-1 in Action. Carrolton, TX: Squadron Signal. ISBN 0-89747-179-2
- Francillon, Rene, J. Vietnam: The War in the Air New York: Arch Cape Press (1987)
- Mesko, Jim, Airmobile: The Helicopter War in Vietnam, Squadron Signal Publications (1984).
- Specifications for 204, 205 and 214 Huey Plus
- Template:Harvard reference
- Mutza, Wayne. UH-1 Huey in Colors. Carrolton, TX: Squadron Signal. ISBN 0-89747-279-9
External links
- The Bell UH-1 Huey at Greg Goebel's AIR VECTORS
- UH-1N USAF fact sheet
- FAS.org Huey profile
- UH-1B history on Mojojets.com
- UH-1H history on Mojojets.com
- Philippine Air Force Huey II Project
- Bell Helicopter Official Huey II site
- An account of a Medal of Honor rescue flying a Green Hornet
Related Content
Related development
- AH-1 Cobra
- UH-1N Twin Huey
- Bell 204/205
- Bell 212
- Bell 214
- Bell 412
- UH-1Y Venom
- Bell 533
- Panha Shabaviz 2-75
Related lists
See also
Fighter aircraft: YFM-1 · P-39 · P-59 · P-63 · XP-77 · XP-83
Commercial Helicopters: 47 · 204 · 205 · 206 · 210 · 212 · 214 · 222 · 230 · 407 · 412 · 417 · 427 · 429 · 430
Military Helicopters: H-13 · UH-1 · 207 · 209 · AH-1 · 309 · YAH-63 · OH-58 · ARH-70
Tiltrotors: V-22 · BA609 · TR918 · QTR
Experimental aircraft: X-1 · X-2 · X-5 · X-20 X-22 · XV-3 · XV-15 · 533 ·
Lists relating to aviation | |
|---|---|
| General | Timeline of aviation · Aircraft · Aircraft manufacturers · Aircraft engines · Aircraft engine manufacturers · Airports · Airlines |
| Military | Air forces · Aircraft weapons · Missiles · Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) · Experimental aircraft |
| Notable incidents and accidents | Military aviation · Airliners · General aviation · Famous aviation-related deaths |
| Records | Flight airspeed record · Flight distance record · Flight altitude record · Flight endurance record · Most produced aircraft |
Category:Military helicopters H-01 Iroquois Category:United States Marine Corps equipment Category:Vietnam War aircraft